During an Olympic bobsled run, the thrill of gravity’s pull, the roar of the crowd, and the blur of ice beneath create an exhilarating experience that demands precision, teamwork, and a touch of daredevilry.
As the sled hurtles down the icy track, a symphony of forces collide. Gravity accelerates it, friction slows it, and centrifugal force pushes it outward. The bobsled’s aerodynamic design slices through the air, reducing drag and maximizing speed.
The Physics of Bobsledding: During An Olympic Bobsled Run

Bobsledding is a thrilling sport that combines speed, precision, and athleticism. It involves teams of athletes navigating a sled down an icy track, reaching incredible speeds while experiencing various physical forces.
Gravity
Gravity is the primary force that propels the bobsled down the track. As the sled descends, the force of gravity pulls it towards the Earth’s center, causing it to accelerate and gain speed.
During an Olympic bobsled run, the metal runners of the sled slide along the ice, creating a unique sound. Metalpoint, a drawing technique that uses a metal stylus on a prepared surface, also creates a distinctive mark. The metal stylus, typically made of silver or lead , scratches the surface, leaving a metallic line.
The resulting artwork has a subtle, delicate quality that captures the essence of the Olympic bobsled run, where speed and precision are paramount.
Friction, During an olympic bobsled run
Friction is the force that opposes the motion of the sled as it slides down the track. This force arises from the interaction between the sled’s runners and the ice surface. Friction slows down the sled, but it is also essential for maintaining control and preventing the sled from skidding off the track.
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is an apparent force that acts on the bobsled as it travels around the curves of the track. This force pushes the sled outwards, away from the center of the curve. Centrifugal force is balanced by the inward force of friction, which keeps the sled on the track.
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics plays a crucial role in bobsled design. The sled’s streamlined shape minimizes air resistance, allowing it to reach higher speeds. The sled’s aerodynamic features also help stabilize it, reducing drag and improving overall performance.
The Bobsled Track
Olympic bobsled tracks are meticulously designed to provide both exhilarating speeds and utmost safety for the athletes. The track layout typically consists of a starting point, numerous curves, and a finish line, all carefully engineered to test the skills and limits of the sledders.
Curves on a Bobsled Track
Bobsled tracks feature a variety of curves, each posing unique challenges to the sledders. The most common types include:
- Parabolic Curves:These curves are shaped like a parabola, with a gradual entry and exit. They allow sleds to maintain high speeds while providing some stability.
- Banked Curves:These curves have a sloped surface that helps keep the sleds upright as they navigate the turns. The banking angle varies depending on the speed and radius of the curve.
- Horseshoe Curves:These are sharp, U-shaped curves that require precise steering and balance. They can significantly reduce sled speeds.
- Chicane Curves:These are a series of closely spaced, alternating curves that force sleds to make quick directional changes.
The combination and sequence of these curves on a track determine the overall difficulty and excitement of the run.
Safety Features on a Bobsled Track
Bobsledding is an inherently dangerous sport, so tracks incorporate numerous safety features to protect athletes:
- Concrete Walls:These line the track to prevent sleds from veering off course and crashing.
- Crash Nets:These are suspended over certain sections of the track to catch sleds that lose control.
- Sprinkler System:This system sprays water on the track to reduce friction and improve sled stability.
- Medical Personnel:Trained medical professionals are stationed along the track to provide immediate assistance in case of an accident.
These safety measures help ensure that bobsledding remains a thrilling yet controlled sport.
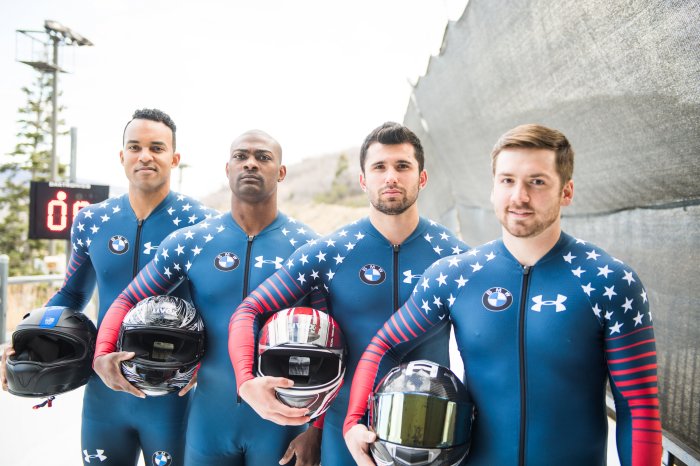
The Bobsled Team
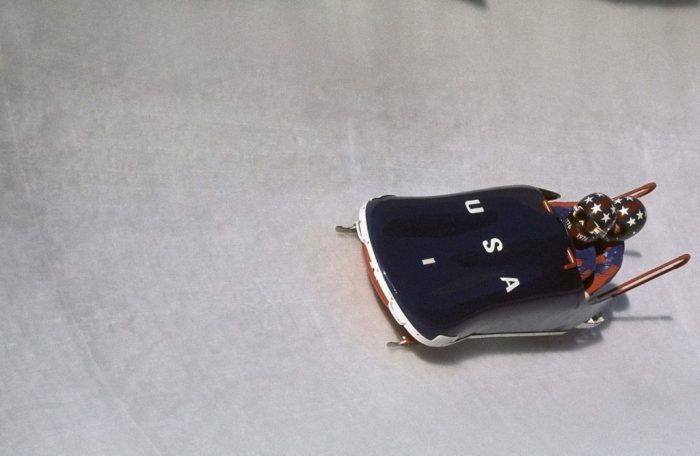
A bobsled team consists of several individuals, each playing a crucial role in achieving a successful run.
The team typically includes the following members:
Driver
- Responsible for steering the bobsled down the track.
- Requires exceptional reflexes, spatial awareness, and decision-making skills.
- Coordinates with the brakeman to control the speed and trajectory of the sled.
Brakeman
- Sits at the back of the bobsled, controlling the speed by applying the brakes.
- Assists the driver in steering and providing stability.
- Communicates with the driver to adjust the sled’s position and speed.
Pushers
- Provide the initial acceleration by pushing the bobsled down the starting track.
- Require strength, power, and coordination.
- Typically consist of two to four athletes.
Teamwork and coordination are paramount in bobsledding. Each member must execute their role seamlessly, communicating effectively and reacting to changing conditions on the track. Extensive training and preparation are essential to develop the skills and teamwork necessary for a successful run.
The Bobsled Equipment
Modern Olympic bobsleds are marvels of engineering, designed to achieve maximum speed and performance on icy tracks. They are constructed using lightweight and durable materials, with aerodynamic features that minimize drag and enhance stability.
Materials and Construction
Bobsleds are typically made of carbon fiber, a lightweight and strong material that provides excellent stiffness and rigidity. The frame of the sled is constructed using a combination of carbon fiber tubes and panels, which are bonded together using advanced adhesives.
The exterior of the sled is covered with a thin layer of fiberglass, which helps to protect the carbon fiber from damage and provides a smooth surface for airflow.
Aerodynamic Features
Bobsleds are designed with a number of aerodynamic features to reduce drag and improve performance. The front of the sled is shaped like a teardrop, which helps to reduce the amount of air resistance encountered by the sled. The sides of the sled are also sloped, which helps to create a smooth flow of air over the surface of the sled.
In addition, the bottom of the sled is equipped with a series of runners that are designed to minimize friction with the ice.
Equipment for Bobsledders
In addition to the bobsled itself, bobsledders also use a variety of equipment to enhance their performance. This equipment includes:
- Helmets: Bobsledders wear helmets to protect their heads from injury in the event of a crash. Helmets are typically made of carbon fiber or fiberglass and are designed to absorb impact energy.
- Suits: Bobsledders wear tight-fitting suits that are designed to reduce drag and improve aerodynamics. Suits are typically made of a lightweight and breathable material, such as Lycra.
- Shoes: Bobsledders wear shoes that are designed to provide good grip on the ice. Shoes are typically made of a rubber compound that is designed to provide traction and stability.
Safety Features
Bobsledding is a dangerous sport, and bobsleds are equipped with a number of safety features to protect the athletes. These features include:
- Roll bars: Bobsleds are equipped with roll bars that are designed to protect the athletes in the event of a rollover. Roll bars are typically made of steel or aluminum and are designed to withstand a significant amount of force.
- Seat belts: Bobsledders are secured in their seats using seat belts. Seat belts are typically made of a strong and durable material, such as nylon, and are designed to keep the athletes in place in the event of a crash.
- Fire extinguishers: Bobsleds are equipped with fire extinguishers to help put out any fires that may occur. Fire extinguishers are typically located in the cockpit of the sled and are easily accessible to the athletes.
The Bobsled Run

An Olympic bobsled run is a thrilling and demanding event that tests the skills, teamwork, and physical endurance of the athletes involved. The run typically consists of several stages, each presenting unique challenges and obstacles that the bobsledders must navigate successfully to achieve the fastest time.
The Start
The bobsled run begins with the start, where the bobsled and its crew are positioned at the top of the track. The start is crucial as it sets the initial momentum and speed for the rest of the run. The bobsledders push off with all their might, generating as much speed as possible before they hop into the sled and begin their descent.
The Track
The bobsled track is a winding, icy chute designed to test the limits of both the bobsled and its crew. It features various curves, straightaways, and obstacles that require precise steering and control. The track is often lined with walls or barriers to prevent the bobsled from derailing, but these can also pose additional challenges if the sled makes contact.
The Bobsled Team
A bobsled team consists of two or four athletes, each with a specific role to play. The driver is responsible for steering the sled and navigating the track, while the brakeman assists with steering and controls the sled’s speed using the brakes.
In a four-man bobsled, two additional athletes known as pushers provide extra momentum at the start and help maintain speed throughout the run.
Techniques for Maximizing Speed
Bobsledders employ various techniques to maximize their speed and minimize their time. These include:
- Aerodynamic positioning: The bobsledders adopt a streamlined position within the sled to reduce air resistance and improve speed.
- Weight distribution: The crew carefully distributes their weight within the sled to optimize balance and handling.
- Cornering techniques: Bobsledders use specific techniques to navigate corners efficiently, such as drifting and counter-steering.
The History of Bobsledding
Bobsledding traces its origins to the late 19th century in Switzerland, where it began as a recreational activity involving wooden sleds steered by ropes. The first organized bobsled race took place in St. Moritz, Switzerland, in 1884.
Bobsledding evolved rapidly in the early 20th century, with the introduction of metal sleds and the development of new steering techniques. The first Olympic bobsled race was held at the 1924 Winter Olympics in Chamonix, France. Since then, bobsledding has become a popular and competitive Olympic sport.
Famous Bobsledders
- Eugenio Monti: Italian bobsledder who won two gold medals and two silver medals in the 1950s and 1960s.
- Andre Lange: German bobsledder who won four gold medals and two silver medals between 2002 and 2010.
- Kaillie Humphries: Canadian bobsledder who won three gold medals and one bronze medal between 2010 and 2022.
The Future of Bobsledding
Bobsledding is a thrilling and competitive sport that has captured the imagination of athletes and spectators alike. As we look ahead, it is exciting to speculate on the future of bobsledding and the potential advancements that may shape this dynamic sport in the years to come.
One area where we can expect significant progress is in bobsled technology. Engineers and designers are constantly pushing the boundaries of innovation to create sleds that are faster, more aerodynamic, and safer. We may see the introduction of new materials and construction techniques that reduce drag and improve handling.
Additionally, advancements in sensor technology could provide real-time data to drivers, helping them optimize their performance.
Track Design
The design of bobsled tracks will also play a crucial role in the future of the sport. New tracks may be built with more challenging and exciting layouts, incorporating features such as tighter turns, higher speeds, and innovative obstacles. These tracks will demand greater skill and precision from drivers and teams, making races even more thrilling.
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends are likely to shape the future of bobsledding. One notable trend is the increasing diversity of athletes participating in the sport. Bobsledding has traditionally been dominated by certain countries and regions, but we are now seeing more and more athletes from a wider range of backgrounds competing at the highest level.
This diversity brings new perspectives and approaches to the sport, fostering innovation and growth.
Another trend is the growing emphasis on athlete training and preparation. Bobsledding is a demanding sport that requires a high level of physical fitness, technical skill, and mental toughness. Athletes are investing more time and resources into their training, using advanced techniques such as data analysis, simulation, and personalized coaching to improve their performance.
Common Queries
What is the most important factor in a successful bobsled run?
Teamwork and coordination are crucial, as each member plays a vital role in maximizing speed and minimizing time.
How fast can a bobsled go?
Olympic bobsleds can reach speeds of over 80 miles per hour (130 kilometers per hour).
What are the safety features incorporated into bobsled tracks?
Tracks have padded walls, escape hatches, and braking systems to ensure the safety of athletes.