Former german african colony crossword delves into the multifaceted history of German colonialism in Africa, shedding light on its motivations, impact, and enduring legacy. From the establishment of German colonies to the rise of independence movements, this narrative unravels the complexities of colonial rule and its far-reaching consequences.
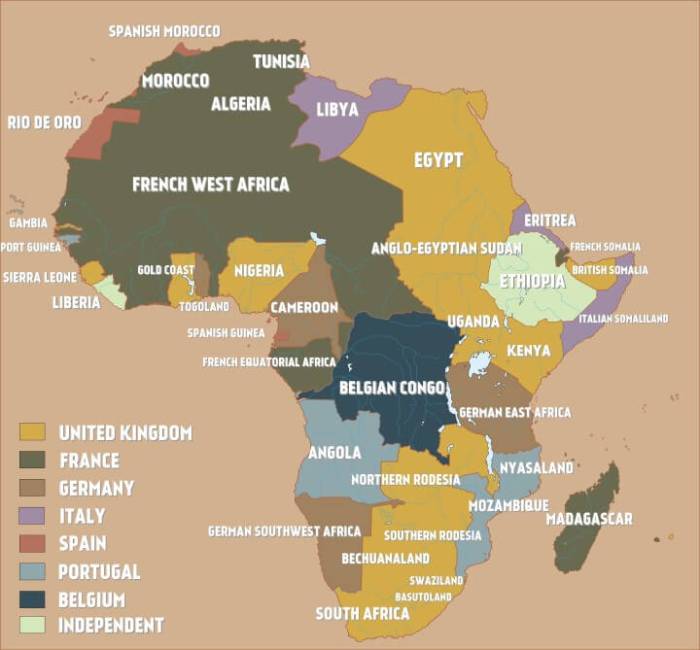
The second paragraph provides a detailed historical overview of German colonial expansion in Africa, examining the factors that drove Germany’s imperial ambitions and the strategies employed to establish and maintain its colonies. It explores the motivations and objectives of German colonialism, the major German African colonies and their respective locations, and the impact of colonial rule on African societies.
Historical Context of German African Colonies
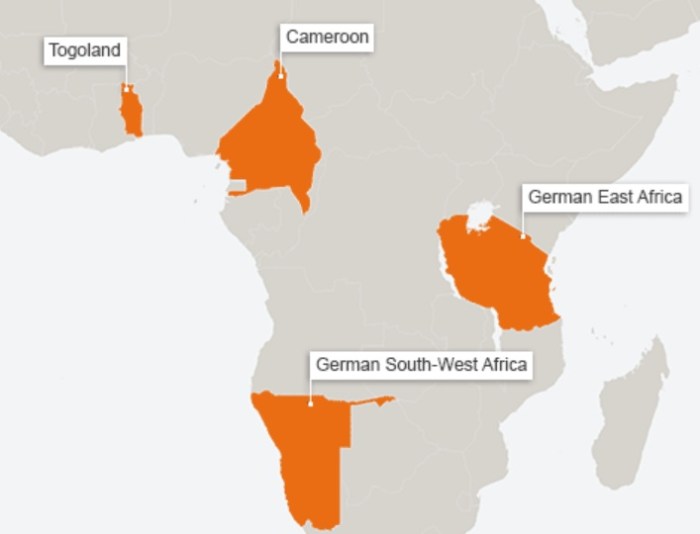
German colonial expansion in Africa began in the late 19th century, driven by a combination of economic, political, and ideological factors. Germany sought to establish colonies as a means of securing raw materials, expanding its markets, and enhancing its international prestige.
The major German African colonies included:
- German East Africa (present-day Tanzania, Rwanda, and Burundi)
- German South West Africa (present-day Namibia)
- Togoland (present-day Togo and part of Ghana)
- Kamerun (present-day Cameroon)
Post-Colonial Era and Independence Movements
German colonial rule in Africa began to decline after World War I, as a result of the defeat of Germany and the rise of nationalist movements in the colonies. Independence movements emerged in the 1950s and 1960s, led by African leaders who sought to end colonial rule and establish independent nations.
Examples of successful independence movements include:
- Tanganyika (now Tanzania) gained independence in 1961.
- Ghana (formerly Gold Coast) gained independence in 1957.
However, some independence movements faced setbacks and challenges, such as the Mau Mau Uprising in Kenya and the Biafran War in Nigeria.
Legacy and Impact of German Colonialism
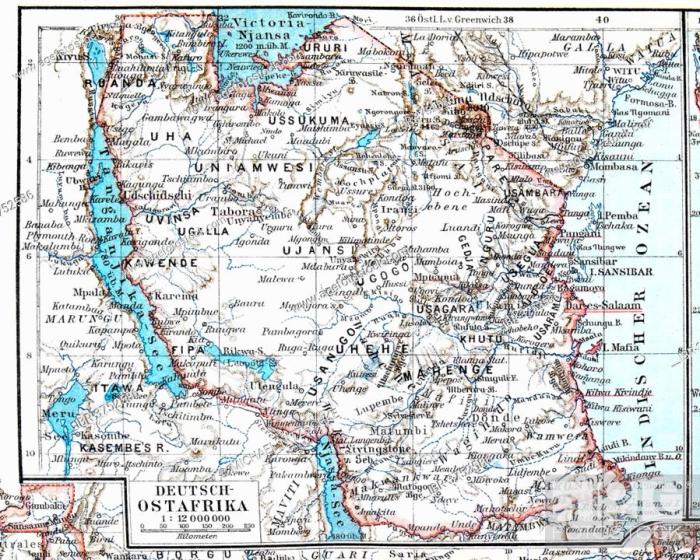
German colonialism had a profound and lasting impact on African societies. The colonial period introduced new technologies, infrastructure, and ideas, but it also led to significant social, economic, and political changes.
The long-term consequences of German colonialism include:
- Economic exploitation and the disruption of traditional economic systems
- Social inequality and the creation of new social hierarchies
- Political instability and the rise of ethnic conflicts
The legacy of German colonialism continues to be debated and contested in contemporary times.
Contemporary Relations between Germany and Former Colonies
Relations between Germany and its former African colonies have evolved over time. In recent decades, Germany has made efforts to address its colonial past and to build new partnerships with African nations.
Efforts made by Germany to address its colonial past include:
- Providing development aid and financial assistance
- Promoting cultural exchange and dialogue
- Supporting efforts to promote reconciliation and healing
However, there remain challenges and tensions in contemporary relations, such as ongoing debates about reparations and the repatriation of cultural artifacts.
Cross-Cultural Exchange and Cultural Heritage
The colonial period in Africa was a time of significant cultural exchange between European and African societies. German colonists introduced new cultural practices, such as Christianity and Western education, while also being influenced by African traditions and beliefs.
Examples of cultural exchange during the colonial period include:
- The adoption of German architectural styles in African cities
- The spread of German language and literature in African societies
- The incorporation of African motifs and designs into German art and crafts
The cultural heritage of German colonialism continues to be reflected in contemporary African societies, shaping cultural practices, traditions, and identities.
FAQ Explained: Former German African Colony Crossword
What were the major German African colonies?
The major German African colonies included German East Africa (present-day Tanzania, Rwanda, and Burundi), German South West Africa (present-day Namibia), Togoland (present-day Togo and part of Ghana), Kamerun (present-day Cameroon), and German New Guinea (present-day Papua New Guinea).
What factors led to the decline of German colonial rule?
The decline of German colonial rule was influenced by a combination of factors, including the growing strength of African independence movements, the impact of World War I, and the changing attitudes towards colonialism within Germany and internationally.
What is the legacy of German colonialism in Africa?
The legacy of German colonialism in Africa is complex and multifaceted, with both positive and negative impacts. It includes the introduction of infrastructure, education, and healthcare, but also the exploitation of resources, suppression of local cultures, and the creation of ethnic tensions.