Unveiling the Layers of the Earth Worksheet Answers: Embark on a comprehensive journey through the Earth’s intricate structure, delving into the composition, characteristics, and significance of each layer. This definitive guide provides an authoritative overview, empowering you with a profound understanding of our planet’s enigmatic interior.
Layers of the Earth: Layers Of The Earth Worksheet Answers
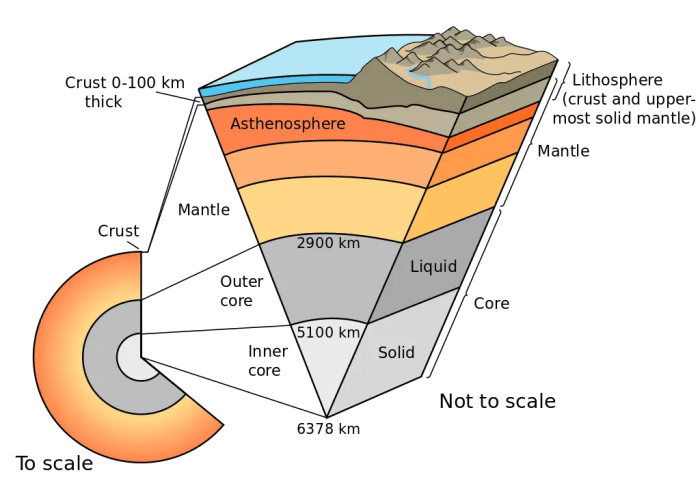
The Earth’s interior is divided into distinct layers based on their composition, physical properties, and behavior. These layers play crucial roles in the planet’s geological processes and overall functioning.
Earth’s Structure
| Layer | Thickness (km) | Density (g/cm³) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crust | 5-70 | 2.7-3.0 | 10-1000 |
| Mantle | 2900 | 3.3-5.5 | 1000-3700 |
| Outer Core | 2200 | 9.9-12.2 | 4400-5200 |
| Inner Core | 1220 | 12.8-13.1 | 5200-6000 |
The transitions between these layers are characterized by abrupt changes in density and seismic wave velocities.
Crust
The Earth’s crust is the outermost layer, ranging in thickness from 5 to 70 kilometers. It is composed primarily of solid rock and is divided into two main types: continental crust and oceanic crust.
Mantle, Layers of the earth worksheet answers
The mantle is the thickest layer, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 kilometers. It is composed of solid rock, predominantly silicate minerals, and is characterized by high temperatures and pressures.
Outer Core
The outer core is a liquid layer that surrounds the inner core. It is composed primarily of iron and nickel and is the source of the Earth’s magnetic field.
Inner Core
The inner core is a solid sphere at the center of the Earth. It is composed primarily of iron and is the hottest part of the planet.
FAQ Compilation
What is the composition of the Earth’s crust?
The Earth’s crust is primarily composed of silicate minerals, such as quartz, feldspar, and mica.
What is the role of the mantle in plate tectonics?
The mantle’s convective currents drive the movement of tectonic plates, leading to earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain formation.
How does the Earth’s outer core generate the magnetic field?
The Earth’s outer core is composed of molten iron, which flows and generates electric currents that create the magnetic field.