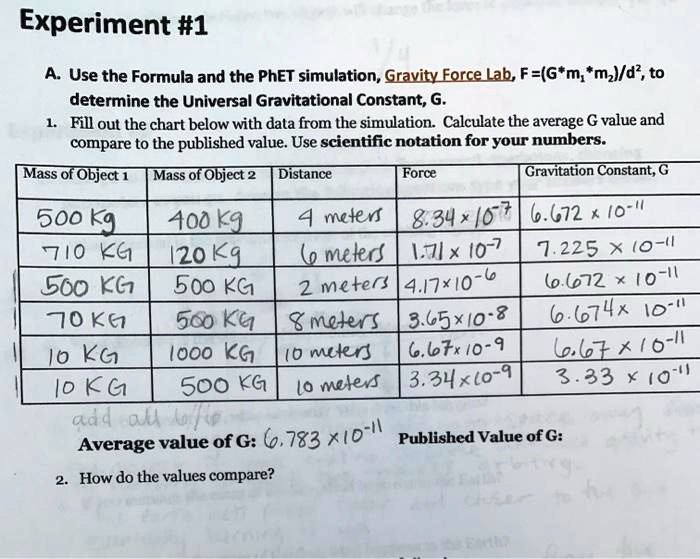
Embark on a scientific expedition with our gravity force simulation answer key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the mysteries of gravity. Dive into the fundamental principles, mathematical equations, and practical applications of this captivating force that shapes our universe.
From the celestial dance of planets to the everyday experience of objects falling, gravity’s influence is omnipresent. Our answer key provides a roadmap for understanding its intricate workings, empowering you to navigate the complexities of this fascinating phenomenon.
1. Definition and Concept of Gravity Force: Gravity Force Simulation Answer Key
Gravity force is a fundamental force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. It is responsible for the movement of celestial bodies, such as planets orbiting stars, and for the objects falling to the ground on Earth.
The strength of gravity force depends on the mass of the objects involved and the distance between them. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. Similarly, the closer two objects are, the stronger the gravitational force between them.
2. Mathematical Representation of Gravity Force
Newton’s law of universal gravitation provides a mathematical formula to calculate the gravitational force between two objects:
F = G
- (m1
- m2) / r^2
where:
- F is the gravitational force (measured in newtons)
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10^-11 N m^2 kg^-2)
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects (measured in kilograms)
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects (measured in meters)
3. Factors Influencing Gravity Force
The strength of gravity force is primarily influenced by two factors:
- Mass:The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull.
- Distance:The closer two objects are, the stronger the gravitational force between them.
For example, the Earth’s gravitational force is stronger than the Moon’s because the Earth has a larger mass. Similarly, the gravitational force between two objects on Earth’s surface is weaker than the gravitational force between the same objects if they were closer together.
4. Applications of Gravity Force
Gravity force has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Space exploration:Gravity force is used to design and operate satellites, rockets, and other spacecraft.
- Engineering:Gravity force is considered in the design and construction of bridges, buildings, and other structures.
- Navigation:Gravity force is used in inertial navigation systems to determine the position and orientation of aircraft, ships, and submarines.
5. Simulations and Modeling of Gravity Force
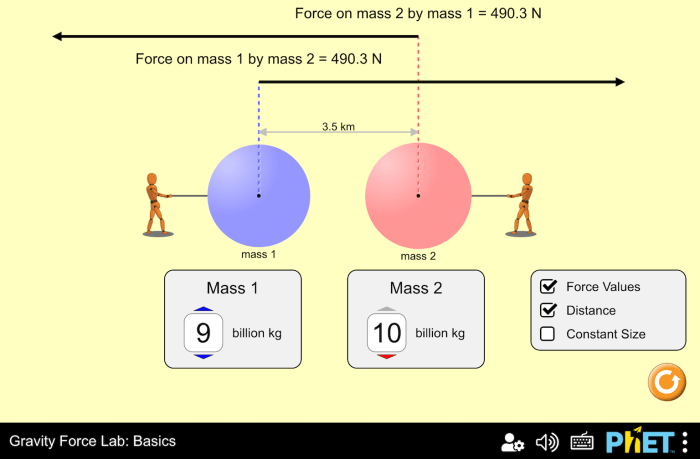
Simulations and modeling are used to study gravity force and its effects in various contexts.
Computer simulations can create virtual environments to model gravitational interactions between objects. These simulations help scientists understand the behavior of celestial bodies, predict the trajectory of spacecraft, and design engineering structures that can withstand gravitational forces.
6. Historical Perspectives on Gravity Force
The concept of gravity force has evolved over time, from ancient theories to modern scientific discoveries.
Aristotle proposed that objects fall to the ground because they are attracted to the center of the Earth. Galileo later demonstrated that objects fall at the same rate regardless of their mass. Newton’s law of universal gravitation provided a mathematical framework to explain the force of gravity.
FAQ Corner
What is the mathematical formula for calculating gravitational force?
F = G – (m1 – m2) / r^2, where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between their centers.
How does mass affect gravity?
The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull.
What are some practical applications of gravity force?
Gravity is used in space exploration to calculate satellite trajectories, in engineering to design bridges and buildings, and in navigation to determine the Earth’s position.