In the intricate network of railway systems, turnouts emerge as crucial elements that orchestrate the smooth flow of trains. As we delve into the realm of que son los apartaderos turnouts, we unravel their multifaceted role, delving into their design, construction, operation, applications, and the cutting-edge advancements that shape their future.
From humble beginnings to sophisticated marvels of engineering, turnouts have evolved to meet the demands of an ever-evolving railway landscape. Their significance lies in their ability to guide trains along complex routes, ensuring efficient movement and enhancing overall safety.
1. Definition of Turnouts
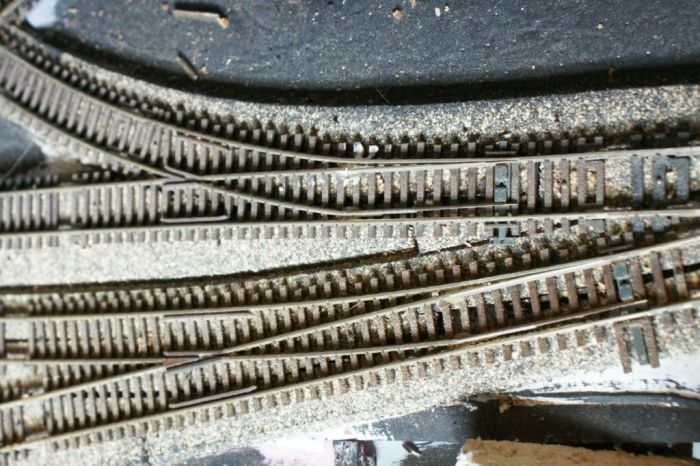

Turnouts, also known as switches or points, are critical components of railway systems that enable trains to change tracks. They provide a means for trains to diverge from one track to another, allowing for flexibility in routing and efficient movement of rail traffic.
Turnouts consist of movable rails that can be adjusted to guide trains in different directions. These rails are operated by point machines or switch levers, which control their alignment. Turnouts are classified into various types based on their function and design, including single slips, double slips, and crossovers.
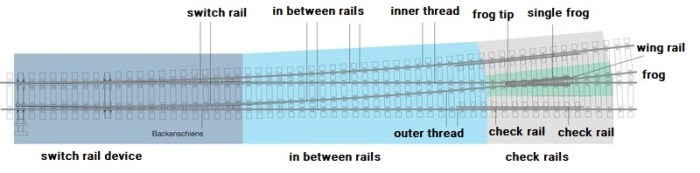
Components of a Turnout
- Points:The movable rails that guide trains in different directions.
- Frogs:The intersection where the rails from different tracks cross.
- Switch Blades:The movable parts of the points that align with the stock rails to create a continuous running surface.
2. Design and Construction of Turnouts: Que Son Los Apartaderos Turnouts
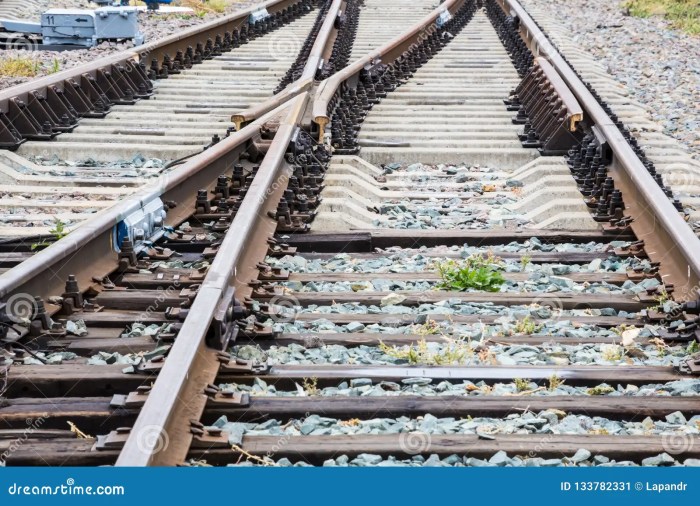

The design of turnouts is influenced by several factors, including the speed of trains, traffic volume, and track geometry. Turnouts are designed to ensure smooth and safe passage of trains while minimizing wear and tear on the rails.
The construction process of turnouts involves track laying, ballasting, and tamping. Track laying involves placing the rails and sleepers in position. Ballasting is the process of filling the spaces between the sleepers with crushed stone or other materials to provide stability.
Tamping is the process of compacting the ballast to ensure a firm and level track bed.
Illustrations or Diagrams
[Insert illustrations or diagrams to demonstrate the design and construction principles of turnouts]
3. Operation and Maintenance of Turnouts
Turnouts are operated by point actuation mechanisms, which can be manual, electric, or hydraulic. The point actuation system ensures that the points are aligned correctly and locked in place to prevent derailments.
Maintenance of turnouts is crucial to ensure their reliable and safe operation. Regular inspections, lubrication, and adjustments are necessary to keep turnouts in good condition. Common turnout failures include point failures, frog wear, and switch blade misalignment. Troubleshooting techniques involve identifying the cause of the failure and taking appropriate corrective actions.
4. Applications and Benefits of Turnouts
Turnouts have various applications in railway networks, including junctions, sidings, and yards. They allow trains to change tracks for different destinations, access maintenance facilities, and create additional track capacity.
The benefits of using turnouts include increased flexibility in routing, reduced train delays, and improved safety. Turnouts enable trains to move efficiently through complex railway networks, reducing congestion and improving overall system performance.
Case Studies or Examples, Que son los apartaderos turnouts
[Provide case studies or examples to illustrate the advantages of turnouts in different railway scenarios]
5. Technological Advancements in Turnouts
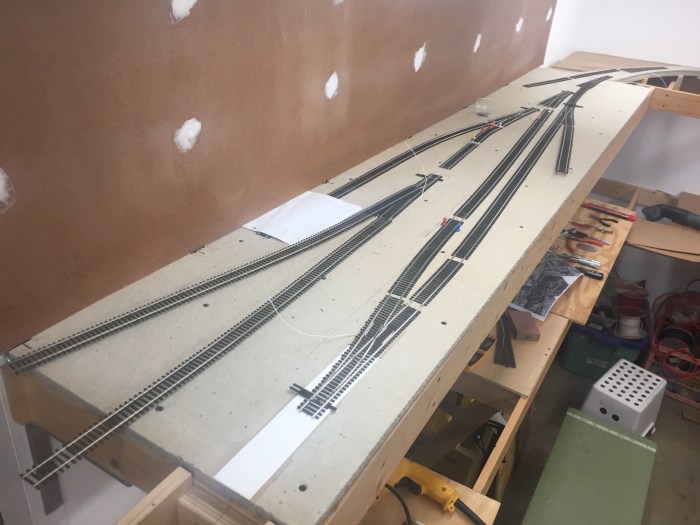

Recent technological advancements have led to the development of automated point actuation systems and condition monitoring systems for turnouts. Automated point actuation systems use sensors and actuators to align and lock the points, improving reliability and reducing the risk of human error.
Condition monitoring systems use sensors to monitor the condition of turnouts, detecting potential problems early on and allowing for proactive maintenance. These advancements have the potential to improve the safety, reliability, and efficiency of railway systems.
Examples or Illustrations
[Provide examples or illustrations to demonstrate the practical applications of these technologies]
FAQ Section
What is the primary function of a turnout?
A turnout, also known as a railway switch, allows trains to transition from one track to another, enabling complex routing and efficient movement within railway networks.
What are the different types of turnouts?
Turnouts come in various forms, including single slips, double slips, and crossovers, each designed for specific operational requirements and track layouts.
How are turnouts designed and constructed?
The design and construction of turnouts involve meticulous planning, considering factors such as speed, traffic volume, and track geometry. The process encompasses track laying, ballasting, and tamping to ensure optimal performance and longevity.