What is a trench block? In the grim trenches of World War I, these unsung heroes played a crucial role in shaping the course of the conflict, offering soldiers a lifeline amidst the relentless onslaught.
These concrete fortifications, often overlooked in the annals of history, were more than just blocks of stone. They were symbols of resilience, innovation, and the desperate struggle for survival in the face of unimaginable horrors.
Historical Context of Trench Blocks
The origins of trench blocks can be traced back to the early 20th century, during the First World War. As trench warfare became more prevalent, the need for effective defensive fortifications grew. Trench blocks emerged as a solution, providing a modular and easily deployable way to construct protective barriers and reinforce existing trenches.
Materials and Construction, What is a trench block
Trench blocks were typically made from concrete, a durable and readily available material. They were cast in various shapes and sizes, with common dimensions being around 2 feet long, 1 foot wide, and 6 inches thick. The blocks were often reinforced with steel rods or wire mesh to enhance their strength and resistance to artillery fire.
So, what exactly is a trench block? It’s basically a piece of reinforced concrete used in building fortifications and military trenches. Now, if you’re prepping for the RN HESI Exit Exam 2023 , you’ll need to know about trench blocks, especially if you’re aiming for a high score.
These blocks played a crucial role in World War I, providing protection for soldiers in the trenches. They’re still relevant today, as they offer a solid and durable way to construct defensive structures.
Construction methods varied depending on the specific design of the trench blocks. In general, they were laid in staggered rows, creating a interlocking wall that could withstand significant pressure. The blocks were typically mortared together or connected using metal pins or clamps.
Role in Defensive Warfare
Trench blocks played a crucial role in defensive warfare during World War I. They were used to construct a variety of defensive structures, including trench walls, bunkers, and machine gun emplacements. The interlocking design allowed for the creation of complex and adaptable fortifications that could be tailored to the specific needs of the battlefield.
Trench blocks provided protection against enemy fire, both from small arms and artillery. They also served as obstacles, slowing down enemy advances and making it difficult for them to breach defensive lines.
Types of Trench Blocks: What Is A Trench Block
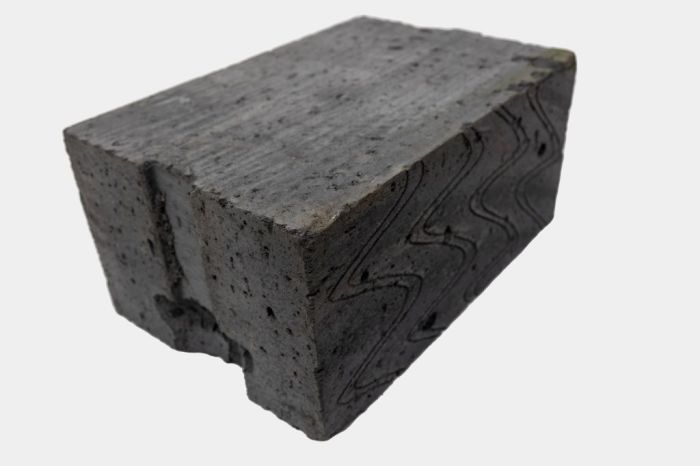

Trench blocks, also known as concrete blocks or fortification blocks, were an essential element in the construction of trenches during World War I. These blocks were designed to provide protection for soldiers against enemy fire and to facilitate the rapid construction of trenches and other defensive structures.
There were several different types of trench blocks used in World War I, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of which type of block to use was often influenced by factors such as the availability of materials, the terrain, and the specific needs of the troops.
Types of Trench Blocks
- Standard Trench Blocks:These were the most common type of trench block used in World War I. They were typically made of concrete and measured approximately 2 feet long, 1 foot wide, and 1 foot high. Standard trench blocks were easy to produce and transport, and they could be used to build a variety of different trench structures.
- Trench Blocks with Embrasures:These blocks had a hole or opening in the front, which allowed soldiers to fire their weapons without exposing themselves to enemy fire. Trench blocks with embrasures were particularly useful for constructing firing positions and machine gun nests.
- Trench Blocks with Corrugated Sides:These blocks had corrugated sides, which made them easier to grip and move. Trench blocks with corrugated sides were also less likely to slip or slide when stacked, which made them more stable and durable.
- Trench Blocks with Handles:These blocks had handles on the sides, which made them easier to carry and move. Trench blocks with handles were particularly useful for constructing trenches in difficult terrain or in areas where there was a lot of enemy fire.
Design and Structure of Trench Blocks
Trench blocks were designed with a specific shape, size, and weight to optimize their functionality and effectiveness. They were typically rectangular or trapezoidal in shape, allowing them to be stacked easily and interlocked to create a stable and robust structure.
The size and weight of trench blocks varied depending on their intended use. Smaller blocks were typically used for the construction of dugouts and shelters, while larger blocks were used for the construction of walls and fortifications. The weight of the blocks ranged from a few kilograms to several hundred kilograms, making them difficult to move by hand but providing excellent protection against enemy fire.
Internal Compartments and Features
Trench blocks often featured internal compartments and features that enhanced their functionality. Some blocks had hollow interiors that could be filled with sand or earth to provide additional protection against bullets and shrapnel. Others had built-in firing ports or loopholes that allowed defenders to fire their weapons without exposing themselves to enemy fire.
The design and structure of trench blocks evolved over time to meet the changing needs of the war. By the end of World War I, trench blocks had become an essential element of trench warfare, providing soldiers with protection, shelter, and the ability to defend their positions effectively.
Deployment and Use of Trench Blocks
Trench blocks were deployed and installed on the battlefield using various methods, each tailored to the specific conditions and tactical requirements. One common method involved digging a trench and then placing the blocks along the sides, creating a protective barrier.
The blocks were typically stacked in layers, with each layer offset from the one below to create a stepped or staggered effect. This arrangement provided additional stability and reduced the likelihood of the blocks being dislodged by enemy fire.
Strategic Advantages
The use of trench blocks offered several tactical and strategic advantages. First, they provided an effective means of quickly constructing defensive positions, allowing troops to establish a fortified line with minimal effort. The blocks were also highly durable, capable of withstanding heavy artillery fire and providing reliable protection for the soldiers within the trenches.
Additionally, trench blocks could be easily modified or adapted to suit specific terrain or tactical situations, making them a versatile and adaptable defensive measure.
Integration into Trench Systems
Trench blocks were an integral part of the overall defensive system of trenches, complementing other fortifications such as barbed wire, sandbags, and machine gun nests. They were often used to create strongpoints or опорные пункты, which were fortified positions designed to hold out against enemy attacks and provide a base for counterattacks.
Trench blocks also served as a barrier against enemy infiltration, preventing the enemy from easily penetrating the trench lines and disrupting the defensive system.
Effectiveness and Impact of Trench Blocks
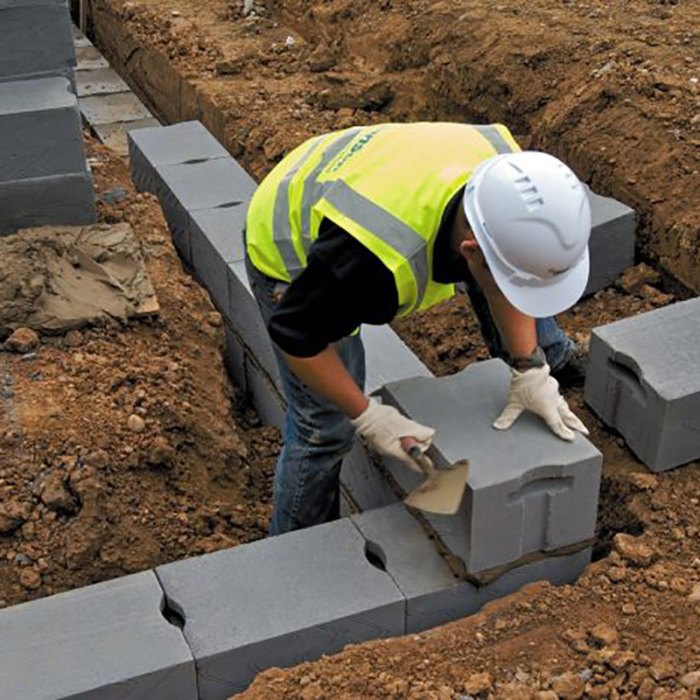

Trench blocks played a crucial role in shaping the course of trench warfare, proving effective in preventing enemy advances and protecting soldiers. Their rugged construction and interlocking design created formidable barriers that hindered the movement of infantry and cavalry. The presence of trench blocks forced attackers to adopt new tactics, such as artillery bombardments and gas attacks, to break through enemy lines.
Psychological Impact
Beyond their physical effectiveness, trench blocks had a significant psychological impact on both attackers and defenders. For attackers, the sight of trench blocks instilled a sense of foreboding and made them wary of advancing. The obstacles represented a formidable barrier that could potentially trap them in a vulnerable position.
Conversely, for defenders, trench blocks provided a sense of security and confidence, knowing that they had a solid barrier protecting them from enemy fire.
Shaping Trench Warfare
The widespread use of trench blocks transformed trench warfare into a more static and protracted conflict. The obstacles made it difficult for either side to gain significant ground, leading to prolonged periods of stalemate. Trench blocks became an integral part of the trench system, contributing to the characteristic trench warfare tactics of sniping, artillery duels, and nighttime raids.
They played a pivotal role in shaping the grim and unforgiving nature of the conflict on the Western Front.
Popular Questions
What were trench blocks made of?
Trench blocks were typically made of concrete, reinforced with steel rods or mesh.
What was the purpose of trench blocks?
Trench blocks were used to construct defensive barriers, providing cover and protection for soldiers from enemy fire.
How were trench blocks used in warfare?
Trench blocks were stacked together to create walls, bunkers, and other defensive structures, forming an intricate network of fortifications.
What was the impact of trench blocks on World War I?
Trench blocks played a significant role in trench warfare, slowing down enemy advances and protecting soldiers, but also contributing to the stalemate and prolonged nature of the conflict.